Enlarged Prostate (BEP)
What is Prostate
The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows from the bladder and out through the penis. One of the main functions of the prostate gland is to produce prostatic fluid, one of the components of semen.
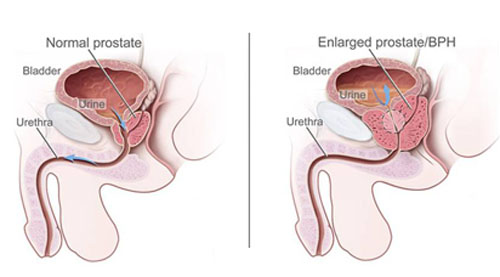
The prostate starts enlarging slowly after the age of 40 and by the age of 70 almost one in every three men have significant symptoms requiring treatment. The enlarged prostate causes compression of urethra.
Symptoms
The key symptoms of enlarged prostate are:
- Weak or intermittent stream of urine
- Hesitancy or difficulty in starting to pass urine
- Need for frequent trips to the toilet, including having to get up several times in the night
- Need to pass urine urgently
- Feeling that the bladder is not empty after urination
- Inability to pass urine completely (retention)
- Repeated urine infection or formation of stone in bladder
Diagnosis
At ACKU, our aim is to understand your bothering symptoms with the help of international scoring system (IPSS), make an accurate diagnosis by detailed examination and necessary tests including Ultrasound and Urine Flow test (Uroflowmetry). This along with your other medical problems and personal and social circumstances will help us in suggesting the best option of treatment. We would also like to ensure that the prostate enlargement is age-related (benign) only and not due to cancer.
1. IPSS (International Prostate Symptom Score) and Quality of Life Score (QOL)
IPSS is a questionnaire designed to determine the intensity of man’s urinary symptoms and help diagnose prostate enlargement. The patient answers seven questions related to common symptoms of prostate enlargement and severity of each symptom is rated from 0 to 5. These numbers added together provide a score that is used to evaluate the condition.IPSS is a questionnaire designed to determine the intensity of man’s urinary symptoms and help diagnose prostate enlargement. The patient answers seven questions related to common symptoms of prostate enlargement and severity of each symptom is rated from 0 to 5. These numbers added together provide a score that is used to evaluate the condition.
QOL is a questionnaire designed to determine the effect of the urinary symptoms on man’s daily routine. This is rated from 1 to 6.
2. Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
The doctor inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the patient’s rectum to feel the surface of the prostate gland through the rectal wall to assess its size, shape, and consistency. Healthy prostate tissue is soft and malignant tissue is firm to hard, and often asymmetrical.
QOL is a questionnaire designed to determine the effect of the urinary symptoms on man’s daily routine. This is rated from 1 to 6.
Uroflowmeter at Panchal Urology Hospital
Uroflowmeter
3. Uroflowmetry (Urine flow test)
With the help of a uroflowmeter, a test is performed which records urine flow to determine how quickly the bladder can be emptied. With a full bladder, the patient urinates into a device that measures the amount of urine, the time it takes for urination, and the rate of urine flow. A reduced flow rate may indicate prostate enlargement.
4. PSA Test
This is a blood test to check the levels of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in a patient who may have BPH. Normal result generally means absence of prostate cancer. Higher level along with abnormal feeling prostate raises the suspicion of prostate cancer and requires further evaluation.
5. Ultrasound test (including post void residue measurement)
This test is performed with full bladder and immediately after urination. At full bladder, the volume of urine is measured and any changes in bladder wall due to prostate enlargement are noted. The shape and size of prostate are also noted. The patient is then asked to urinate and the residual urine is determined by ultrasound. Post void residue (PVR) less than 50 ml generally indicates adequate bladder emptying and measurements of 100 to 200 ml or higher often indicate blockage.
Treatment
Generally, early problem is controlled with medicines to relax prostate muscles or reduce the size. Medication is required on a long term basis, otherwise symptoms and problems would recur. Generally the improvement in symptoms and urine flow is significantly less with medicines than with surgery.
When the symptoms progress, fail to respond to medicines or patient develops retention, stones or repeated infections, surgery is required to remove part of prostate to open urine passage.
ACKU Facilities
World class Endoscopic Prostatic Surgery which includes TURP, THULEP, TUIP, TUVP is been done with humanitarian touch at affordable cost, with motherly nursing care in post operative ward.
ACKU is the first to introduce in Bangladesh LASER Ennucleation of prostate by Thulium Laser 120W Revolix (THULEP).
In this operation bleeding is very minimum, no blood is required during operation, no chance of complication, no bladder wash is required after operation. Patient can go home after 2 days. Even sexual function remain ok after operation.
Quick Links
Contact Centre
- General enquiries
+88 02 9145809
+88 02 9145808
+88 01746 344179 - Request a call back
Can we call you back at a more convenient time - Email us
Send us an email enquiry and we will get back to you.

